How to Manage a Raw Vegan Diet meal plan: Signifies and Risky.
To successfully following a raw vegan diet food, it’s a very important to preparing adequately to ensure you get the vitamins and minerals you need for your health. You can help prevent vitamin B12, vitamin D, or calcium deficiencies.
A Food List of Which Food to Eat and Which to Avoid on a Raw Vegan Diet
Which to Eat Raw Vegan
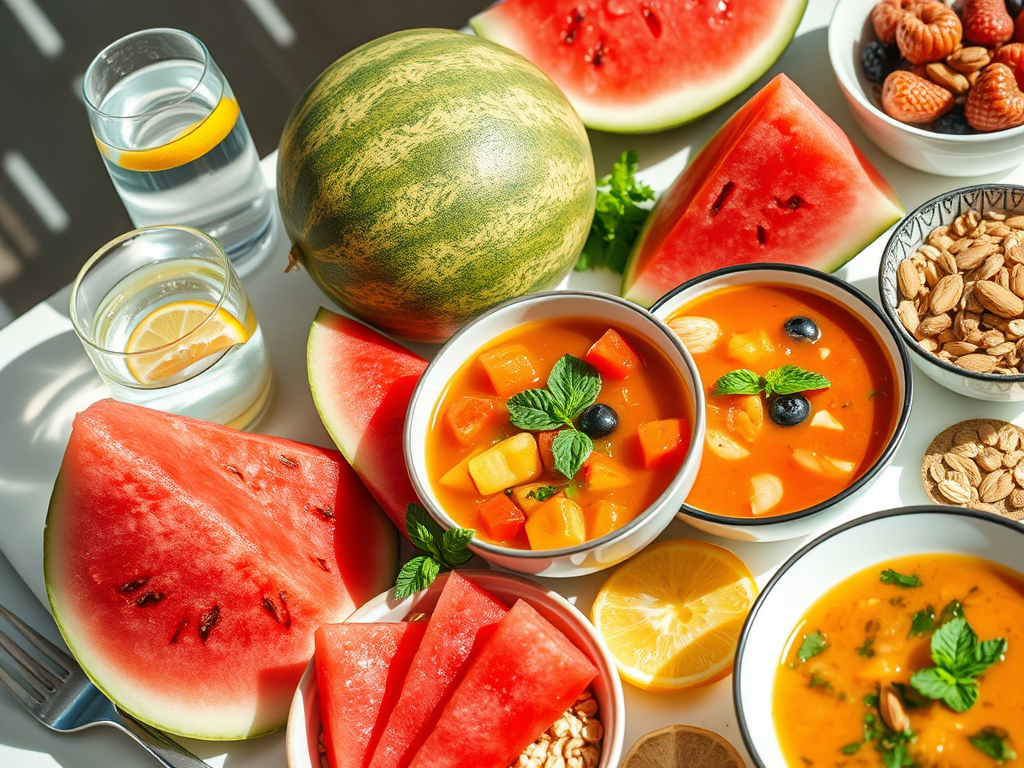
- Fresh, dried, juiced or dehydrated fruits
Dried fruits are much higher in sugar and have a higher glycemic index compared to fresh fruit, making them a not-so-healthy choice. Dried fruits are full of nutrients, easy to pack, and count toward your daily fruit recommendation!
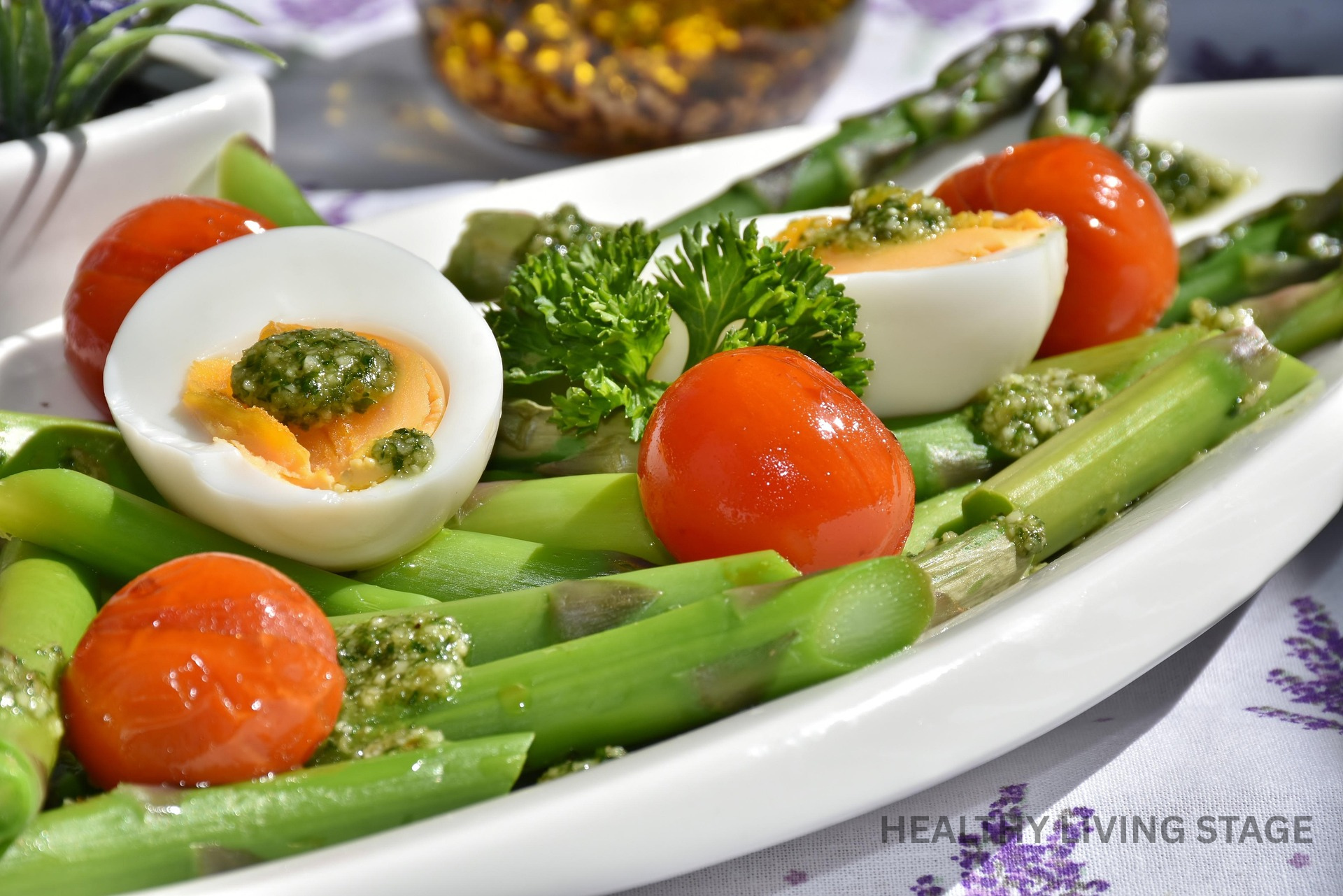
- Raw, juiced or dehydrated vegetables
Fresh vegetables are rich in nutrients, juices transforms these nutrients into a drinkable form, while dehydrating helps to preserve the vegetables and maintain a significant portion of their nutritional benefits.
- Raw nuts and seeds
- Uncooked grains and legumes (sprouted or soaked)
- Raw nut milks
- Raw nut butters
- Cold-pressed oils
- Fermented foods like miso, kimchi and sauerkraut
- Seaweed
- Some sweeteners, such as pure maple syrup and unprocessed raw cacao powder
- Condiments, including vinegars and unpasteurized raw soy sauce
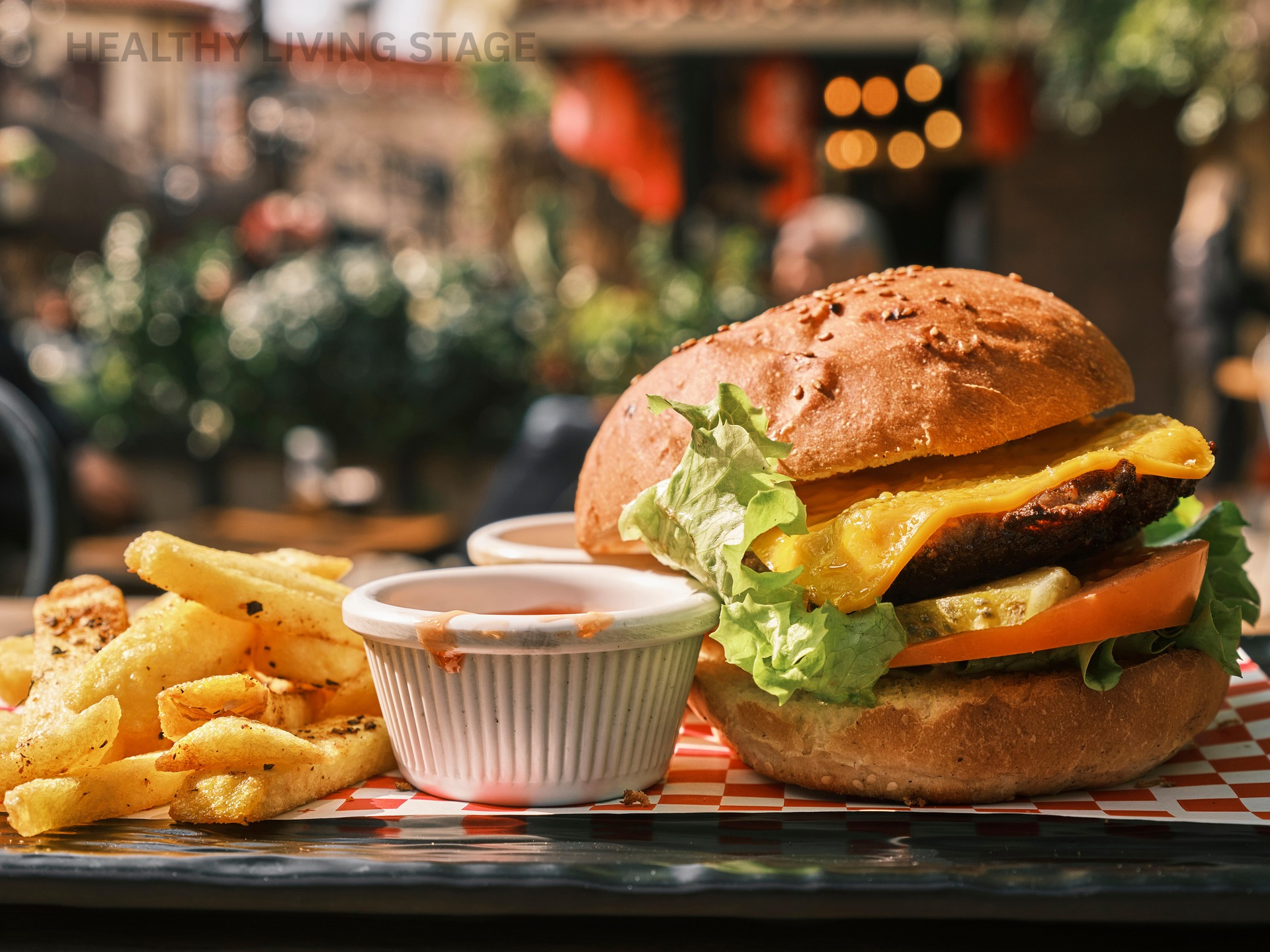
Which to Avoid Raw Vegan
- Cooked fruits, vegetables, grains and legumes
- Baked goods
- Roasted nuts and seeds
- Refined oils
- Salt
- Refined sugars and flours
- Pasteurized juices
- Coffee and tea
- Alcohol
- Processed foods and snacks, such as chips and pastries.


